Introducing Roger Clayton, a healthcare maestro with two decades of unparalleled experience in medical insurance. As the visionary behind Medinscoverage, Roger's mission is to demystify...Read more
Medicare is a government-funded healthcare program that provides coverage to millions of Americans. However, navigating the different aspects of Medicare can be confusing and overwhelming. One aspect of Medicare that many people are not familiar with is MIPS, or the Merit-based Incentive Payment System.
MIPS is a program that was created by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to incentivize healthcare providers to improve the quality of care they provide to Medicare beneficiaries. The program is designed to reward providers who meet certain quality and performance standards, while also penalizing those who do not. In this article, we will take a closer look at what MIPS is and how it works, so that you can better understand how it may impact your healthcare.
MIPS stands for Merit-based Incentive Payment System. It is a program that aims to improve the quality of care provided to Medicare beneficiaries while also controlling healthcare costs. MIPS replaces three existing programs: the Physician Quality Reporting System, the Value-based Payment Modifier, and the Medicare Electronic Health Record Incentive Program. MIPS measures healthcare providers’ performance in key areas such as quality, cost, and improvement activities. Based on their performance, providers may receive a positive or negative payment adjustment from Medicare.
Understanding MIPS for Medicare
Medicare has a lot of rules and regulations that can be confusing, especially when it comes to reporting quality measures. The Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) was created to streamline the reporting process and provide incentives for doctors and healthcare providers to improve the quality of care they deliver to Medicare patients. In this article, we’ll explain what MIPS is, how it works, and what it means for healthcare providers.
What is MIPS?
MIPS is a program that is part of the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA), which was signed into law in 2015. The goal of MIPS is to tie Medicare payments to the quality of care that providers deliver to their patients. MIPS replaces several other quality reporting programs, including the Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), the Value-Based Payment Modifier (VM), and the Medicare Electronic Health Record (EHR) Incentive Program.
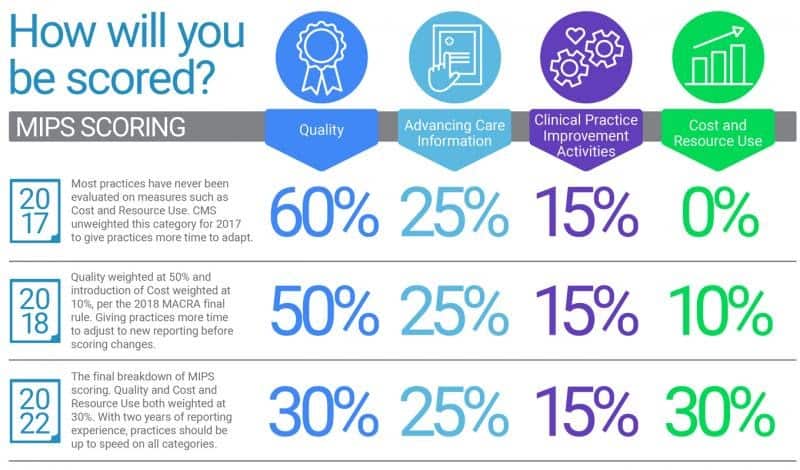
Under MIPS, healthcare providers are measured in four categories: Quality, Cost, Improvement Activities, and Promoting Interoperability. The scores in each category are combined to create a total MIPS score, which determines whether providers receive a bonus payment, a penalty, or no adjustment to their Medicare payments.
How Does MIPS Work?
To participate in MIPS, healthcare providers must submit data on quality measures, improvement activities, and promoting interoperability. The data is then used to calculate their MIPS score, which determines their payment adjustment.
The Quality category makes up 45% of the total MIPS score and measures the quality of care delivered to patients. Providers must report on at least six quality measures, including at least one outcome measure, and the data is compared to national benchmarks.
The Cost category makes up 15% of the total MIPS score and measures the cost of care delivered to patients. Providers do not need to submit any data for this category as it is calculated automatically using Medicare claims data.
The Improvement Activities category makes up 15% of the total MIPS score and measures the efforts providers make to improve the quality of care delivered to patients. Providers must complete at least four activities from a list of more than 100 options.
The Promoting Interoperability category makes up 25% of the total MIPS score and measures the use of technology to improve patient care. Providers must report on a set of measures related to interoperability, health information exchange, and patient engagement.
Benefits of MIPS
Participating in MIPS can have several benefits for healthcare providers. First, it provides a financial incentive to improve the quality of care delivered to Medicare patients. Providers who score high on their MIPS score can receive a bonus payment, while those who score low may receive a payment penalty.
Second, MIPS simplifies the quality reporting process by consolidating several programs into one. Providers only need to report on one set of measures, rather than multiple sets for different programs.
Finally, MIPS provides feedback to providers on their performance. Providers receive a scorecard that shows how they performed in each category, which can help them identify areas for improvement.
MIPS vs. Alternative Payment Models (APMs)
MIPS is not the only program under MACRA that ties Medicare payments to quality of care. Alternative Payment Models (APMs) are another option for healthcare providers. APMs are payment models that offer financial incentives for delivering high-quality, cost-effective care.
The main difference between MIPS and APMs is that APMs require providers to take on financial risk. Providers who participate in APMs are eligible for higher bonus payments, but they must also take on the risk of financial losses if they do not meet certain quality and cost targets.
Conclusion
MIPS is an important program for healthcare providers who participate in Medicare. It provides a financial incentive to improve the quality of care delivered to patients and simplifies the quality reporting process. By understanding how MIPS works and participating in the program, providers can improve the care they deliver to their patients and receive financial rewards for their efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Mips for Medicare?
Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) was passed by Congress in 2015, which introduced a new payment system for Medicare called the Quality Payment Program (QPP). Under QPP, there are two tracks: the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) and the Advanced Alternative Payment Models (APMs). MIPS is a program that rewards or penalizes eligible healthcare providers based on their performance in four categories: Quality, Promoting Interoperability, Improvement Activities, and Cost.
MIPS is a value-based payment system that aims to improve the quality of care and reduce healthcare costs by incentivizing providers to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care. MIPS replaces three existing Medicare programs: the Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), the Value-Based Payment Modifier (VBPM), and the Medicare Electronic Health Record (EHR) Incentive Program.
Who is eligible for MIPS?
MIPS is for eligible healthcare providers who bill Medicare Part B. Eligible providers include physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, certified registered nurse anesthetists, and groups that include such professionals. To be eligible for MIPS, healthcare providers must meet certain thresholds, such as billing over $90,000 in Medicare Part B charges per year or seeing over 200 Medicare patients per year.
How is the MIPS score calculated?
The MIPS score is calculated based on a provider’s performance in the four categories mentioned earlier. Each category has a different weight, with Quality accounting for 45% of the total score, Promoting Interoperability accounting for 25%, Improvement Activities accounting for 15%, and Cost accounting for 15%. The total score ranges from 0 to 100, and providers with a score of 30 or higher can earn a positive payment adjustment.
What are the payment adjustments under MIPS?
Under MIPS, eligible healthcare providers can earn a positive, negative, or neutral payment adjustment based on their performance. The payment adjustment is applied to the Medicare Part B fee schedule amount for covered professional services. In 2021, the maximum payment adjustment is +/- 9%. Providers who earn a score of 0 to 29.9 will receive a negative payment adjustment, providers who earn a score of 30 to 69.9 will receive a neutral payment adjustment, and providers who earn a score of 70 or higher will receive a positive payment adjustment.
How can healthcare providers prepare for MIPS?
Healthcare providers can prepare for MIPS by reviewing the program requirements and performance categories, assessing their current performance, and identifying areas for improvement. Providers can also participate in QPP support programs, such as the QPP Resource Center, the QPP Service Center, and the QPP Learning Network. It is important for providers to stay up-to-date with program changes and deadlines to ensure they are meeting the requirements and maximizing their payment adjustments.
Introduction to Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS)
In conclusion, MIPS, or the Merit-Based Incentive Payment System, is a program created by Medicare to encourage healthcare providers to deliver high-quality care. This program uses a scoring system based on several performance categories to determine the payment adjustments made to Medicare reimbursements.
The goal of MIPS is to improve the quality, efficiency, and effectiveness of healthcare services provided to patients. By offering financial incentives to providers who deliver high-quality care, Medicare hopes to reduce healthcare costs while improving patient outcomes.
Overall, MIPS is an important program that plays a significant role in the healthcare industry. Providers who participate in MIPS have the opportunity to not only improve their patient outcomes but also increase their Medicare reimbursements. As healthcare continues to evolve, MIPS will likely continue to play a critical role in incentivizing providers to deliver high-quality care.
Introducing Roger Clayton, a healthcare maestro with two decades of unparalleled experience in medical insurance. As the visionary behind Medinscoverage, Roger's mission is to demystify the labyrinth of healthcare coverage, empowering individuals to make well-informed decisions about their well-being. His profound industry knowledge has been the cornerstone in crafting the website's exhaustive resources, offering users indispensable guidance and tools for their healthcare needs.
More Posts