Introducing Roger Clayton, a healthcare maestro with two decades of unparalleled experience in medical insurance. As the visionary behind Medinscoverage, Roger's mission is to demystify...Read more
If you have a disability, you may be wondering if you qualify for Medicare or Medicaid. These two programs can help cover the cost of healthcare, but they have different eligibility requirements. Understanding which program you may be eligible for can be confusing, but it is important to know so you can get the healthcare you need.
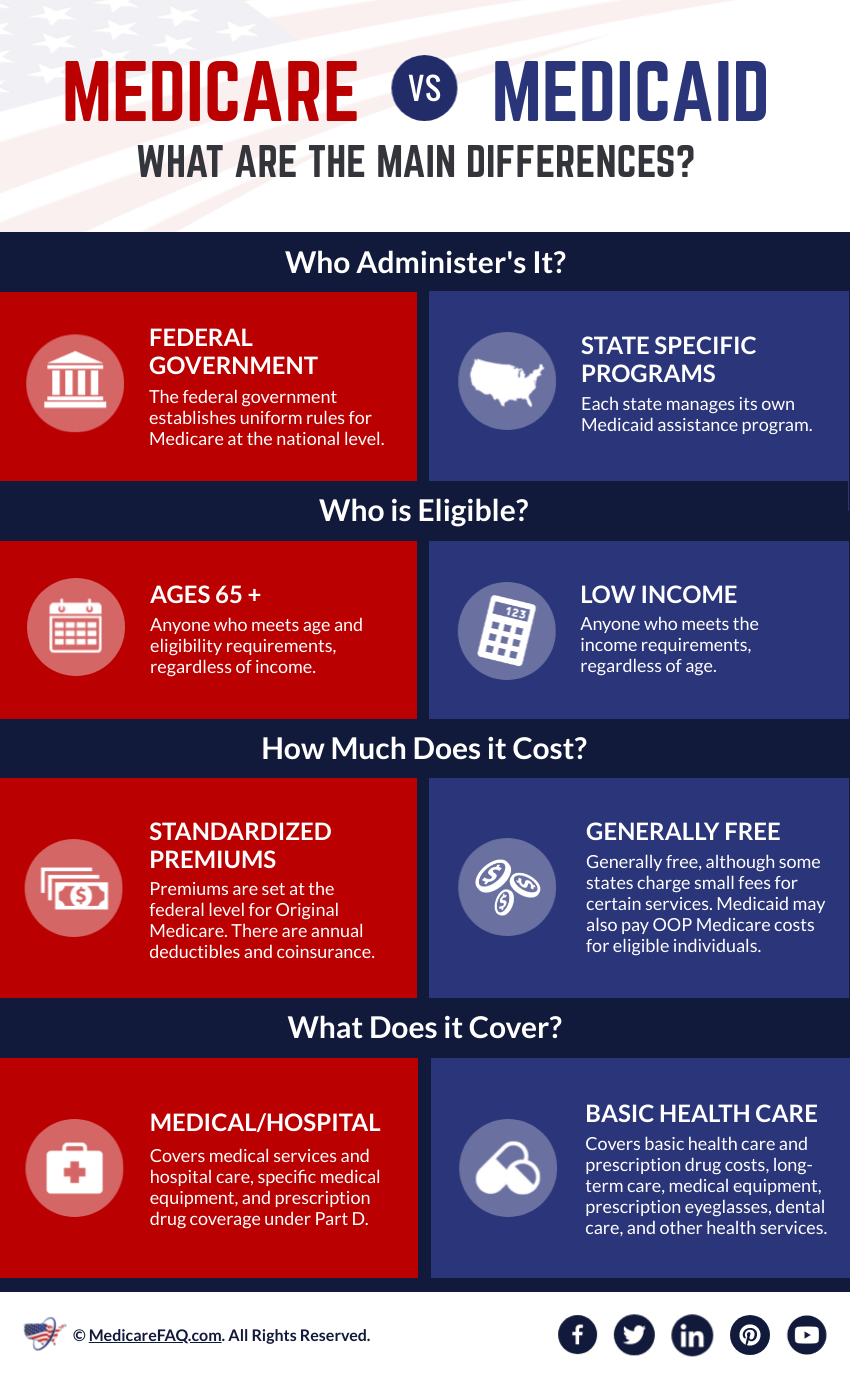
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for people who are 65 or older, as well as people with certain disabilities. Medicaid, on the other hand, is a joint federal and state program that provides healthcare coverage for low-income individuals and families, including those with disabilities. In this article, we will explore the eligibility requirements for both programs and help you determine which one you may be eligible for if you have a disability.
If you qualify for Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) or Supplemental Security Income (SSI), you may also be eligible for Medicare or Medicaid. SSDI recipients become eligible for Medicare after a two-year waiting period. SSI recipients automatically qualify for Medicaid in most states. Medicaid can help with medical expenses, while Medicare offers health insurance coverage. It’s important to note that eligibility requirements and coverage vary by state and program.
Contents
- Do You Get Medicare or Medicaid With Disability?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Question 1: What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
- Question 2: Do all people with disabilities qualify for Medicare or Medicaid?
- Question 3: Can you receive both Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) and Medicare?
- Question 4: What services are covered by Medicare and Medicaid for people with disabilities?
- Question 5: Can I choose between Medicare and Medicaid if I have a disability?
- Can You Qualify for Social Security Disability Insurance and Medicaid at the Same Time?
Do You Get Medicare or Medicaid With Disability?
If you have a disability, you may be eligible for either Medicare or Medicaid. However, it can be confusing to understand which program you may qualify for and what benefits each program provides. In this article, we will explore the differences between Medicare and Medicaid for people with disabilities.
What is Medicare?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage to individuals who are 65 years or older, people with end-stage renal disease, and those with certain disabilities. To qualify for Medicare based on disability, you must have received Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) for at least 24 months or have End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) or Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS).
There are four parts to Medicare: Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D. Part A covers hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, and hospice care. Part B covers doctor visits, outpatient care, and preventive services. Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, is an alternative to traditional Medicare and is provided by private insurance companies. Part D covers prescription drug costs.
What is Medicaid?
Medicaid, on the other hand, is a joint federal and state program that provides healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families. Eligibility for Medicaid varies by state, but most states provide coverage to individuals with disabilities who meet specific income requirements.
Medicaid covers a wide range of healthcare services, including hospital stays, doctor visits, prescription drugs, and long-term care. In addition to healthcare services, Medicaid may also cover services such as transportation to medical appointments and home health aides.
Benefits of Medicare for People with Disabilities
If you are eligible for Medicare based on disability, there are several benefits that you may be entitled to. Medicare can provide you with access to a wide range of healthcare services, including hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription drugs. You may also have access to preventive services such as cancer screenings and annual wellness visits.
In addition, Medicare may provide coverage for durable medical equipment (DME) such as wheelchairs, walkers, and oxygen tanks. Medicare also covers certain types of therapy services such as physical therapy and occupational therapy.
Benefits of Medicaid for People with Disabilities
Medicaid can provide comprehensive healthcare coverage to people with disabilities who may not be able to afford healthcare services otherwise. Medicaid covers a wide range of healthcare services, including hospital stays, doctor visits, prescription drugs, and long-term care.
In addition to healthcare services, Medicaid may also cover services such as transportation to medical appointments, home health aides, and personal care services. Medicaid may also provide coverage for assistive technology and home modifications that can help people with disabilities live independently.
Medicare vs. Medicaid for People with Disabilities
While both Medicare and Medicaid provide healthcare coverage to people with disabilities, there are some key differences between the two programs. Medicare is a federal program that provides coverage to individuals who meet certain eligibility requirements based on age, disability, or medical condition. Medicaid, on the other hand, is a joint federal and state program that provides coverage to low-income individuals and families.
One of the biggest differences between Medicare and Medicaid is cost. Medicare is funded by the federal government and is partially funded by payroll taxes, while Medicaid is jointly funded by the federal government and individual states. Medicaid may also require cost-sharing for certain services, such as copayments or deductibles.
Another difference between Medicare and Medicaid is coverage. While both programs provide coverage for healthcare services, Medicaid may provide additional benefits that Medicare does not cover, such as transportation to medical appointments and home health aides.
Conclusion
If you have a disability, it is important to understand the healthcare coverage options available to you. Medicare and Medicaid are two programs that can provide comprehensive healthcare coverage to people with disabilities, but there are some key differences between the two programs. Before making a decision about which program to enroll in, it is important to compare the benefits and costs of each program to determine which one is right for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage for people who are 65 years or older or have a qualifying disability. Medicaid is a state-run program that provides healthcare coverage for people with low income and limited resources.
While Medicare is available to all eligible individuals regardless of income, Medicaid has specific eligibility requirements that vary by state. Some people may be eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid, known as “dual eligibility.”
Question 2: Do all people with disabilities qualify for Medicare or Medicaid?
Not all people with disabilities qualify for Medicare or Medicaid. To be eligible for Medicare, you must have a qualifying disability and be under 65 years of age. For Medicaid, eligibility varies by state and is based on income and resources. Some disabilities may automatically qualify for Medicaid, such as those who receive Supplemental Security Income (SSI) benefits.
If you have a disability and are not sure if you qualify for Medicare or Medicaid, you can contact your local Social Security office or state Medicaid agency for more information.
Question 3: Can you receive both Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) and Medicare?
If you are approved for SSDI benefits, you will automatically become eligible for Medicare after receiving disability benefits for two years. However, there are some exceptions to this rule for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as end-stage renal disease.
It is important to note that SSDI and Medicaid are two separate programs, and receiving SSDI does not automatically qualify you for Medicaid.
Question 4: What services are covered by Medicare and Medicaid for people with disabilities?
Medicare and Medicaid both cover a wide range of healthcare services for people with disabilities, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription drugs, and medical equipment. Medicaid may also cover additional services such as home healthcare, personal care services, and assistive technology.
It is important to check with your healthcare provider or state Medicaid agency to determine what specific services are covered under your plan.
Question 5: Can I choose between Medicare and Medicaid if I have a disability?
If you are eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid, you can choose to enroll in one or both programs. Medicare is the primary payer for healthcare services, and Medicaid may cover additional costs not covered by Medicare.
If you are unsure which program is right for you, it is recommended to speak with a healthcare provider or a representative from your local Social Security or Medicaid office to discuss your options.
Can You Qualify for Social Security Disability Insurance and Medicaid at the Same Time?
In conclusion, being disabled can be a challenging experience, but it doesn’t have to be financially draining. Medicare and Medicaid are two government programs that can provide much-needed financial assistance to those who need it. While they are different programs with different eligibility requirements, they both offer crucial benefits that can help disabled individuals access healthcare and other essential services.
If you’re disabled and wondering if you qualify for Medicare or Medicaid, it’s essential to understand the differences between the two programs. Medicare is available to individuals aged 65 and older, while Medicaid is designed for individuals with low income and limited resources. However, if you’re disabled and under 65, you may still be eligible for Medicare if you receive Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) benefits.
Overall, whether you qualify for Medicare or Medicaid with a disability, both programs offer critical support to help you manage your healthcare costs and access essential services. By understanding the eligibility requirements and benefits of each program, you can make an informed decision about which program is right for your needs and get the financial assistance you need to live a full and healthy life.
Introducing Roger Clayton, a healthcare maestro with two decades of unparalleled experience in medical insurance. As the visionary behind Medinscoverage, Roger's mission is to demystify the labyrinth of healthcare coverage, empowering individuals to make well-informed decisions about their well-being. His profound industry knowledge has been the cornerstone in crafting the website's exhaustive resources, offering users indispensable guidance and tools for their healthcare needs.
More Posts