Introducing Roger Clayton, a healthcare maestro with two decades of unparalleled experience in medical insurance. As the visionary behind Medinscoverage, Roger's mission is to demystify...Read more
Are you approaching retirement age and wondering when you’ll be eligible for Medicare insurance? Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage to millions of Americans over the age of 65. However, eligibility requirements can vary depending on your individual situation.
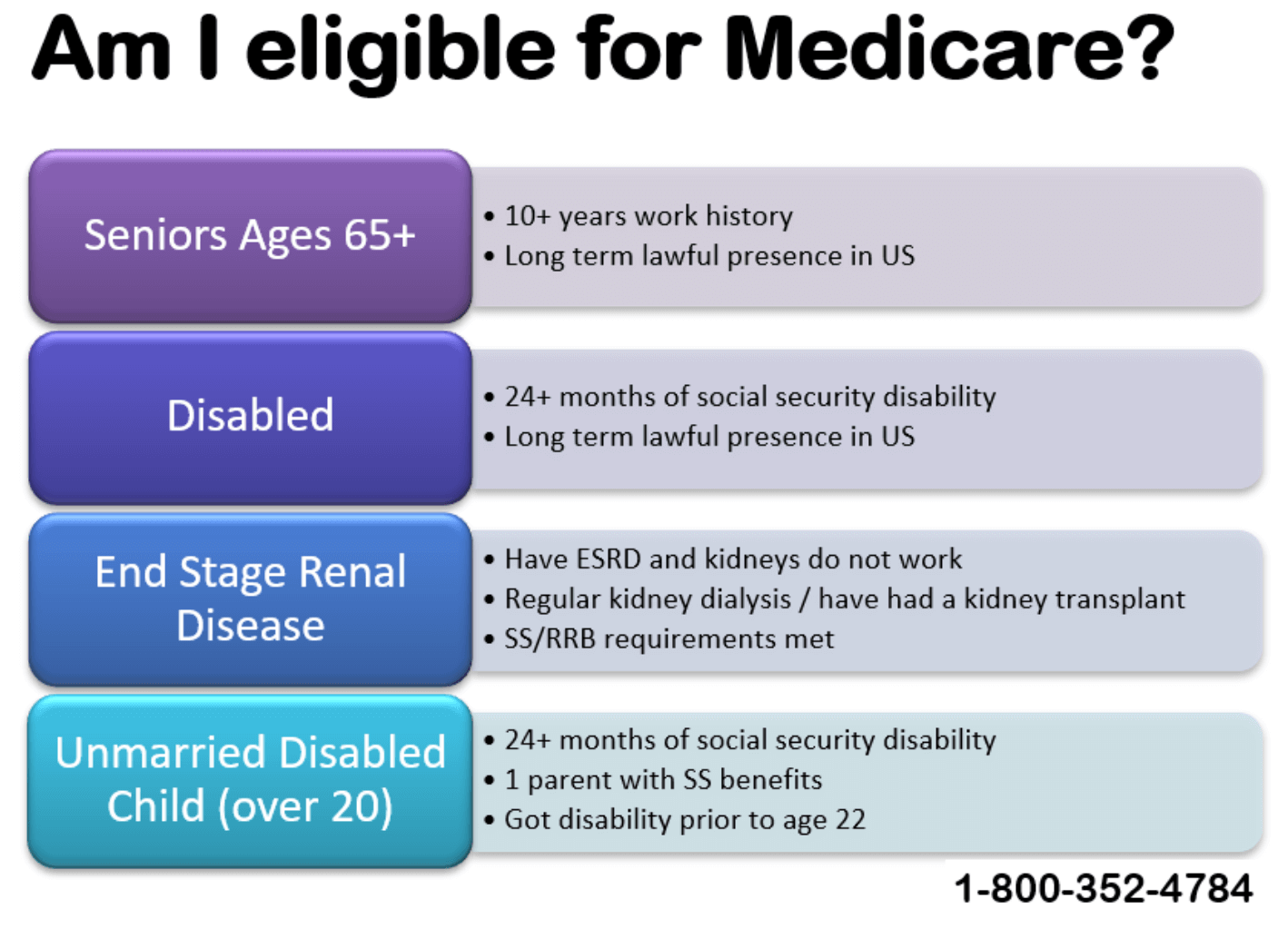
Generally, you are eligible for Medicare if you are 65 years old or older, a permanent resident of the United States, and have paid into the Medicare system through payroll taxes for at least 10 years. If you are younger than 65, you may still be eligible if you have certain disabilities or medical conditions. It’s important to understand the eligibility requirements to ensure you receive the coverage you need.
You are eligible for Medicare insurance when you turn 65 years old, or if you have a disability or end-stage renal disease. You can enroll in Medicare during your Initial Enrollment Period (IEP), which begins three months before your 65th birthday month and ends three months after. If you miss your IEP, you can enroll during the General Enrollment Period (GEP), which runs from January 1 to March 31 each year.
When Am I Eligible for Medicare Insurance?
If you are approaching age 65 or have a disability, you may be wondering when you are eligible for Medicare insurance. Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage to those who meet certain criteria. In this article, we will discuss when you may be eligible for Medicare and what you need to know to enroll.
Age-Based Eligibility
The most common way to become eligible for Medicare is based on your age. You can enroll in Medicare when you turn 65 years old, regardless of whether or not you are retired. You can enroll in Medicare during the three months before your 65th birthday, the month of your birthday, and the three months after your birthday. This seven-month period is known as your Initial Enrollment Period (IEP).
If you miss your IEP, you may be subject to a late enrollment penalty. The penalty is added to your monthly premium for Part B coverage. The penalty amount increases the longer you wait to sign up for Part B. However, if you are still working and have group health coverage, you may be able to delay enrolling in Part B without penalty.
Disability-Based Eligibility
If you have a disability, you may be eligible for Medicare before age 65. You must have received Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) or Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) disability benefits for at least 24 months. Once you have received disability benefits for 24 months, you will automatically be enrolled in Medicare.
If you have Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, you will be automatically enrolled in Medicare the same month that your disability benefits begin.
Enrollment Options
If you are eligible for Medicare, you have several enrollment options. You can enroll in Original Medicare, which includes Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance). You can also enroll in a Medicare Advantage plan, which is offered by private insurance companies and provides additional benefits not covered by Original Medicare.
To enroll in Medicare, you can visit the Social Security Administration website or visit your local Social Security office. You can also enroll by calling Social Security or completing a paper application.
Medicare Benefits
Medicare provides a range of benefits to eligible individuals. Original Medicare covers many medically necessary services, including hospital stays, doctor visits, and preventive care. Medicare Advantage plans typically offer additional benefits, such as prescription drug coverage, dental, and vision care.
In addition to Original Medicare and Medicare Advantage, there are also other Medicare programs that offer additional benefits to eligible individuals, such as Medicare Supplement plans and Medicare Part D prescription drug plans.
Medicare vs. Medicaid
Medicare and Medicaid are two different programs that provide healthcare coverage. Medicare is a federal program that provides coverage to eligible individuals based on age or disability. Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides coverage to low-income individuals and families.
While there are some similarities between the two programs, there are also some key differences. Medicare is generally available to all individuals who meet the eligibility requirements, while Medicaid is only available to individuals who meet certain income and asset requirements.
Medicare vs. Private Health Insurance
Medicare and private health insurance are two different options for healthcare coverage. Private health insurance is typically offered by employers or purchased on the individual market. Medicare is a federal program that provides coverage to eligible individuals based on age or disability.
There are some key differences between the two options. Private health insurance plans may offer more flexibility in terms of provider networks and coverage options. Medicare, on the other hand, provides standardized coverage and may offer more affordable options for individuals with health conditions.
Medicare Costs
While Medicare provides coverage for many healthcare services, there are still costs associated with the program. You will pay a premium for Part B coverage, as well as any additional premiums for Medicare Advantage or Medicare Supplement plans.
You may also be responsible for deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance for certain services. However, there are programs available to help low-income individuals with these costs, such as the Medicare Savings Program and Extra Help.
Important Dates to Remember
There are several important dates to remember when it comes to Medicare enrollment. Your IEP is the seven-month period surrounding your 65th birthday, during which you can enroll in Medicare. If you miss your IEP, you may be subject to a late enrollment penalty.
You can also make changes to your Medicare coverage during the Annual Enrollment Period (AEP), which runs from October 15 to December 7 each year. During this time, you can switch from Original Medicare to a Medicare Advantage plan, switch from one Medicare Advantage plan to another, or enroll in or change your Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage.
Conclusion
Medicare provides valuable healthcare coverage to eligible individuals. Whether you are approaching age 65 or have a disability, it is important to understand when you may be eligible for Medicare and what your options are for enrolling in the program. By understanding the enrollment process, benefits, and costs associated with Medicare, you can make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Medicare insurance provides healthcare coverage for Americans aged 65 and older. Here are some common questions about eligibility for Medicare insurance.
When can I enroll in Medicare?
You can enroll in Medicare during the Initial Enrollment Period (IEP), which is a seven-month period that begins three months before your 65th birthday and ends three months after your 65th birthday. If you miss your IEP, you can enroll during the General Enrollment Period (GEP), which runs from January 1 to March 31 each year. However, if you enroll during the GEP, your coverage won’t start until July 1 of that year.
It’s important to note that if you’re enrolled in Social Security, you’ll be automatically enrolled in Medicare Part A and Part B when you turn 65, unless you opt out of Part B.
What if I’m under 65 but have a disability?
If you’re under 65 and have been receiving Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) for at least 24 months, you’ll automatically be enrolled in Medicare. Your coverage will begin on the 25th month of receiving SSDI. If you have End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) or Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), you may be eligible for Medicare before the 24-month waiting period.
If you have a disability but aren’t receiving SSDI, you’ll need to apply for Medicare during the same enrollment periods as those who are 65 and older.
What if I’m still working when I turn 65?
If you’re still working when you turn 65 and have employer-sponsored health insurance, you may not need to enroll in Medicare immediately. However, it’s important to check with your employer to see if they require you to enroll in Medicare. If they don’t require it, you can enroll in Medicare later without penalty during a Special Enrollment Period (SEP).
If your employer has fewer than 20 employees, Medicare will be your primary insurance and your employer-sponsored insurance will be secondary. If your employer has 20 or more employees, your employer-sponsored insurance will be primary and Medicare will be secondary.
What if I missed my Initial Enrollment Period?
If you missed your Initial Enrollment Period and don’t have a Special Enrollment Period, you can enroll in Medicare during the General Enrollment Period. However, you may have to pay a late enrollment penalty for Part A, Part B, or both. The penalty amount will depend on how long you went without coverage.
If you missed your Initial Enrollment Period but have a Special Enrollment Period, you won’t have to pay a late enrollment penalty as long as you enroll during your SEP.
What if I need help paying for Medicare?
If you have a limited income and resources, you may be eligible for help paying for Medicare through the Medicare Savings Programs (MSPs). The MSPs can help pay for your Part A and Part B premiums, deductibles, copays, and coinsurance.
If you have a very low income, you may also be eligible for Extra Help with your prescription drug costs through the Low-Income Subsidy (LIS) program.
Who Qualifies for Medicare?
In conclusion, understanding when you are eligible for Medicare insurance is crucial for securing your healthcare needs. Whether you are turning 65 or have a qualifying disability, knowing the enrollment periods and deadlines is vital for avoiding late enrollment penalties and gaps in coverage.
It is important to note that Medicare offers a range of coverage options, including Original Medicare, Medicare Advantage, and prescription drug plans. Each plan has its own benefits and costs, so it is essential to research and compare the options available to you to find the best fit for your healthcare needs and budget.
Ultimately, enrolling in Medicare insurance is a significant decision that requires careful consideration and planning. By understanding your eligibility, coverage options, and enrollment deadlines, you can take control of your healthcare and ensure that you have the coverage you need to stay healthy and protected.
Introducing Roger Clayton, a healthcare maestro with two decades of unparalleled experience in medical insurance. As the visionary behind Medinscoverage, Roger's mission is to demystify the labyrinth of healthcare coverage, empowering individuals to make well-informed decisions about their well-being. His profound industry knowledge has been the cornerstone in crafting the website's exhaustive resources, offering users indispensable guidance and tools for their healthcare needs.
More Posts